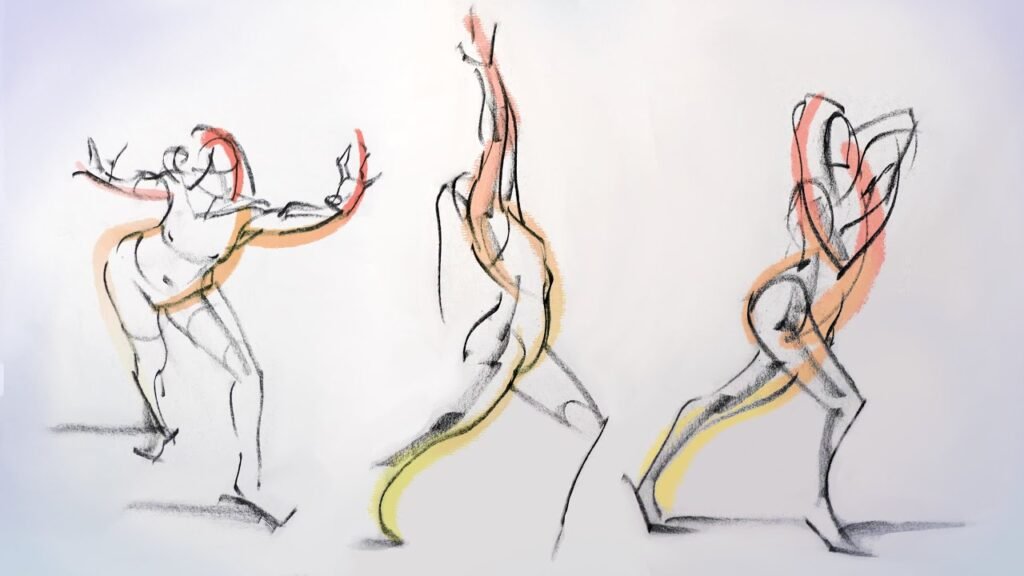Gesture drawing plays a foundational role in sketching, offering artists a dynamic approach to capturing movement, energy, and form. This technique emphasizes the essence of a subject rather than precise details, making it an essential practice for artists of all levels. Whether you are sketching a live model, a moving animal, or an imagined character, gesture drawing helps you convey life and motion in your work.

What Is Gesture Drawing?
Gesture drawing involves quick, loose sketches that focus on the subject’s overall pose, action, and flow. Typically, these sketches are completed in under two minutes, forcing artists to prioritize the subject’s core movement over intricate details.
- Purpose: It is not about creating a polished piece but about understanding the subject’s structure and energy.
- Simplicity: Artists often use sweeping lines and minimal strokes, capturing the subject’s movement and posture.
- Application: Gesture drawing is commonly used in figure drawing, character design, and animation.
Capturing Movement and Energy
Gesture drawing excels at representing the rhythm and vitality of a subject. Instead of focusing on static outlines, this method emphasizes the dynamic nature of movement.
- Motion Over Detail: By simplifying forms into flowing lines, artists can convey the subject’s action and direction effectively.
- Action Lines: These central lines form the backbone of the gesture, showing how the body or subject moves through space.
- Vitality: The quick pace of gesture drawing imbues sketches with spontaneity and life, enhancing the emotional impact of your work.
Improving Observation Skills
Gesture drawing sharpens an artist’s ability to observe and interpret their subject. The time constraint pushes you to identify key elements quickly, such as balance, weight, and proportion.
- Focus on Essentials: Artists learn to eliminate distractions and prioritize the most important aspects of a pose.
- Improved Perception: With practice, gesture drawing trains your eyes to see subtle relationships in form and movement.
- Adaptability: Whether sketching a person, animal, or object, this skill translates across various artistic disciplines.
Building Confidence in Line Work
Frequent gesture drawing builds confidence in your lines, helping you create bold, intentional strokes. Hesitant lines often reflect uncertainty, but gesture practice encourages a free, decisive approach.
- Looseness and Freedom: Artists often find that the fluidity of gesture drawing releases them from the pressure of perfection.
- Foundation for Detail: Confident gesture lines serve as a strong base for refining a drawing into a detailed work.
- Expressiveness: Over time, your gestures will naturally become more expressive and reflective of your unique style.
Applications of Gesture Drawing
Gesture drawing is not just a practice tool; it has practical applications across many art forms.
- Figure Drawing: Essential for capturing human poses, gesture drawing is widely used in life-drawing sessions.
- Animation: Animators rely on gesture drawing to depict movement and action convincingly.
- Character Design: Artists often start with gesture sketches to explore poses and personality traits.
- Storyboarding: Quick, gestural sketches help plan scenes and convey the narrative flow in films and comics.
How to Practice Gesture Drawing
To make the most of gesture drawing, it’s important to approach it with a clear focus and a willingness to experiment.
- Set a Timer: Begin with 30-second or one-minute poses to train your speed and efficiency. Gradually increase the time for more complex gestures.
- Use Reference Material: Sketch from live models, online pose libraries, or even moving subjects like dancers or athletes.
- Focus on Movement: Avoid getting bogged down by details. Concentrate on the subject’s overall energy and flow.
- Experiment with Tools: Use pencils, charcoal, or digital media to explore different textures and effects.
Benefits of Gesture Drawing
Regular gesture drawing practice offers numerous benefits that extend beyond sketching.
- Improved Anatomy Understanding: By simplifying forms, artists gain a better grasp of how body parts interact.
- Enhanced Creativity: The fluid nature of gesture drawing encourages experimentation and reduces creative block.
- Faster Workflow: Artists become adept at laying down foundational sketches quickly, improving efficiency.
Conclusion
Gesture drawing is a powerful tool for any artist, blending observation, movement, and energy into quick yet impactful sketches. By prioritizing action over precision, this technique lays the groundwork for dynamic, expressive art. Regular practice not only enhances technical skills but also fosters creativity, confidence, and a deeper connection with your subject.